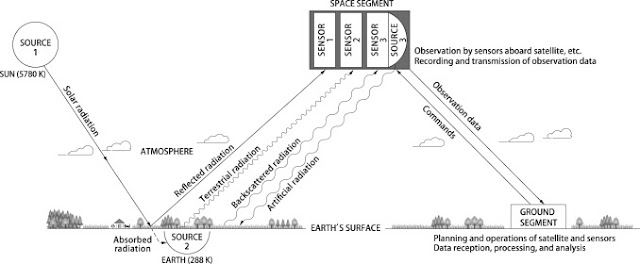
Definition of remote sensing Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites. Remote sensing is the science of obtaining the physical properties of an area without being there.It allows users to capture, visualize, and analyze objects and features on the Earth’s surface. Remote that means something which is not exactly in contact or physical contact, Sensing means getting information, data something like temperature, pressure, photograph, etc. Remote sensing is the process of acquiring information, detecting, analyzing, monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by recording it is reflected and emitted radiation energy without having any physical contact with the object under study. This is done by capturing the reflected radiation/energy. "Remote sensing is the science (and to some extent, art) of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in cont...