|
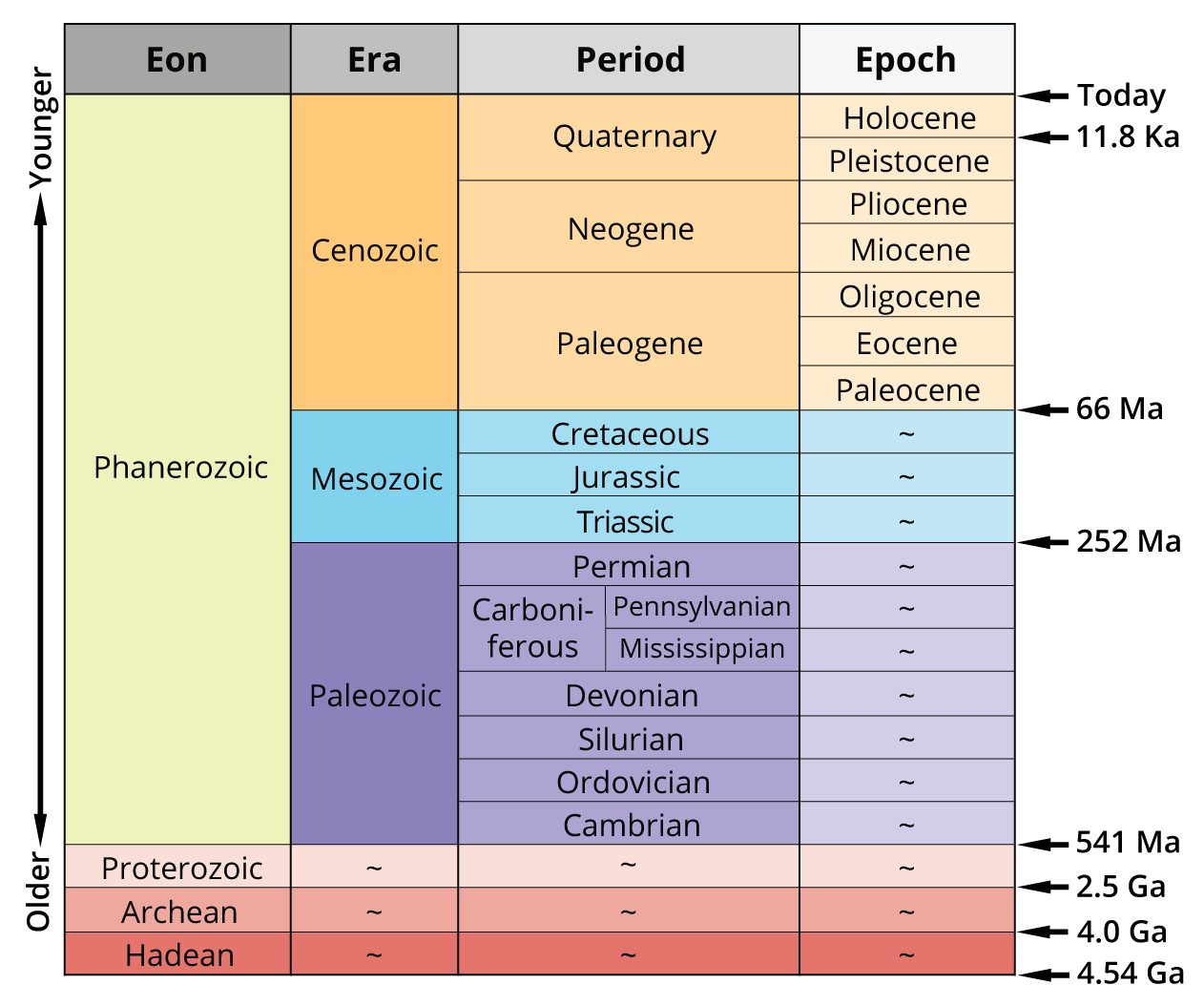
Eon
|
Era
|
Period
|
Epoch
|
Major Geologic Milestones
|
|
Phanerozoic
|
Cenozoic
|
Quaternary
(0-1.6 million yrs BP)
|
Holocene
(Present-10,000 yrs BP)
|
Modern humans develop. Pleistocene Ice Age Interglacial.
|
|
Pleistocene
(10,000 -1,600,000 yrs BP)
|
Pleistocene Ice Age. Extinction of many species of large mammals and
birds.
|
|
Tertiary
|
Pliocene
(1.6-5.3 million yrs BP)
|
Development of hominid bipedalism. Cascade Mountains began forming.
Climate cooling.
|
|
Miocene
(5.3-24 million yrs BP)
|
Chimpanzee and hominid lines evolve. Extensive glaciation in
Southern Hemisphere. Climate cooling.
|
|
Oligocene
(24-37 million yrs BP)
|
Browsing mammals and many types of modern plants evolve. Creation of
the Alps and Himalaya mountain chains. Volcanoes form in Rocky Mountains.
|
|
Eocene
(37-58 million yrs BP)
|
Primitive monkeys evolve and Himalayas began forming. Australian
plate separates from Antarctica. Indian plate collides with Asia.
|
|
Paleocene
(58-65 million yrs BP)
|
Rats, mice, and squirrels evolve. Shallow continental seas become
less widespread.
|
|
Mesozoic
|
Cretaceous
(65-144 million yrs BP)
|
|
First flowering plants, greatest dinosaur diversity, Cretaceous Mass
Extinction (65 m BP), and Andes Mountains form.
Africa and South America begin to separate. Climate cooling because of
mountain building. Shallow seas have extensive distribution.
|
|
Jurassic
(144-208 million yrs BP)
|
First birds and mammals appear. Nevadian Mountains form. Large areas
of the continents covered by shallow seas. Climate generally warm and
stable with little seasonal or latitudinal variation. Shallow seas
expanding.
|
|
Triassic
(208-245 million yrs BP)
|
First dinosaurs. Extensive deserts exist in continental interiors.
Climate warm. Shallow seas limited in distribution.
|
|
Paleozoic
|
Permian
(245-286 million yrs BP)
|
Permian Mass Extinction. Reptiles become more diverse. Climate cold
at beginning of the Permian then warms. Average elevation of landmasses at their
highest shallow seas less extensive.
|
|
Pennsylvanian
(286-320 million yrs BP)
|
First reptiles appear.Winged insects evolve. Occasional glaciation
in Southern Hemisphere.
|
|
Mississippian
(320-360 million yrs BP)
|
Primitive ferns and insects evolve. Forests appear and become
dominant. Mountain building producing arid habitats in the interior of some
continents.
|
|
Devonian
(360-408 million yrs BP)
|
First amphibians and trees appear. Appalachian Mountains form.
Extinction of primitive vascular plants. Landmasses generally increasing in
altitude. Climate cooling.
|
|
Silurian
(408-438 million yrs BP)
|
Major extinction event occurs. First land plants and insects.
Continents are generally flat. Tectonic uplift begins.
|
|
Ordovician
(438-505 million yrs BP)
|
First fish and fungi. Greatest extent of shallow seas. Climate
becoming warmer.
|
|
Cambrian
(505-551 million yrs BP)
|
Invertebrates become common. Fossilization of the Burgess Shale.
Large areas of shallow seas near the equator. Climate was warm.
|
|
Proterozoic
(551-2500 million yrs BP)
|
Also known as Precambrian
|
Eukaryotic cell organisms develop. First multicellular organisms.
Changes in the lithosphere created major land masses and extensive shallow
seas.
|
|
Archean
(2500-3800 million yrs BP)
|
Slow development of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
First single-celled prokaryotic organisms.
|
|
Hadean
(3800-4600 million yrs BP)
|
Earth's oldest rocks come from the end of this Eon.
|

Comments
Post a Comment