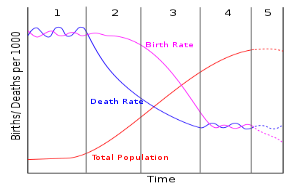
Demographic Transition Model (DTM): Stages of Demographic Transition Model
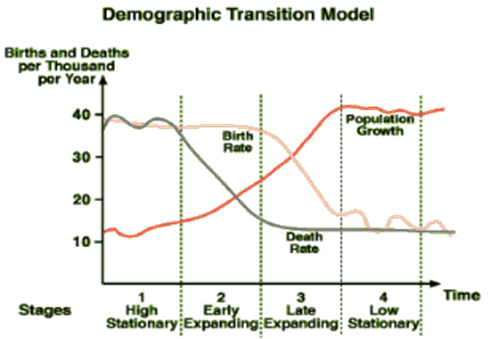
Stages of Demographic Transition Model The changes in population growth rates and the effect on population can be shown on the Demographic Transition Model (Population Cycle): This can be divided into four stages: Stage 1 - High Fluctuating Birth Rate and Death rate are both high. Population growth is slow and fluctuating. The birth Rate is high as a result of:, Lack of family planning High Infant Mortality Rate: putting babies in the 'bank' Need for workers in agriculture Religious beliefs Children as economic assets The death Rate is high because of: High levels of disease Famine Lack of clean water and sanitation Lack of health care War ...