Definition of Remote Sensing/What is Remote Sensing
Definition of remote sensing
- Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites.
- Remote sensing is the science of obtaining the physical
properties of an area without being there.It allows users to capture,
visualize, and analyze objects and features on the Earth’s surface.
- Remote that means something which is not exactly in contact or physical contact, Sensing means getting information, data something like temperature, pressure, photograph, etc.
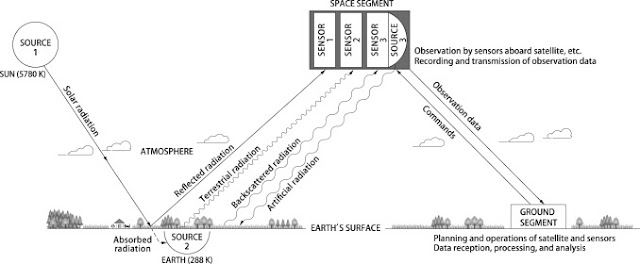
- Remote sensing is the process of acquiring information, detecting, analyzing, monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by recording it is reflected and emitted radiation energy without having any physical contact with the object under study. This is done by capturing the reflected radiation/energy.
- "Remote sensing is the science (and to some extent, art) of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This is done by sensing and recording reflected or emitted energy and processing, analyzing, and applying that information."
- Remote sensing is a type of geospatial technology that samples emitted and reflected electromagnetic (EM) radiation from the Earth’s terrestrial, atmospheric, and aquatic ecosystems in order to detect and monitor the physical characteristics of an area without making physical contact. This method of data collection typically involves aircraft-based and satellite-based sensor technologies, which are classified as either passive sensors or active sensors.
- Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about an object or phenomenon by measuring emitted and reflected radiation. There are two primary types of remote sensing instruments -- active and passive.
- Remote sensing is the acquiring of information from a distance. NASA observes Earth and other planetary bodies via remote sensors on satellites and aircraft that detect and record reflected or emitted energy. Remote sensors, which provide a global perspective and a wealth of data about Earth systems, enable data-informed decision making based on the current and future state of our planet.


Comments
Post a Comment